Base of all data objects. More...
#include <mitkBaseData.h>
Public Types | |
| typedef BaseData | Self |
| typedef itk::DataObject | Superclass |
| typedef itk::SmartPointer< Self > | Pointer |
| typedef itk::SmartPointer < const Self > | ConstPointer |
Public Member Functions | |
| virtual const char * | GetClassName () const |
| const mitk::TimeSlicedGeometry * | GetTimeSlicedGeometry () const |
| Return the TimeSlicedGeometry of the data as const pointer. | |
| mitk::TimeSlicedGeometry * | GetTimeSlicedGeometry () |
| Return the TimeSlicedGeometry of the data as pointer. | |
| const mitk::TimeSlicedGeometry * | GetUpdatedTimeSlicedGeometry () |
| Return the Geometry3D of the data. | |
| virtual void | Expand (unsigned int timeSteps) |
| Expands the TimeSlicedGeometry to a number of TimeSteps. | |
| const mitk::Geometry3D * | GetUpdatedGeometry (int t=0) |
| Return the Geometry3D of the data at time t. | |
| mitk::Geometry3D * | GetGeometry (int t=0) const |
| Return the geometry, which is a TimeSlicedGeometry, of the data as non-const pointer. | |
| virtual void | UnRegister () const |
| Helps to deal with the weak-pointer-problem. | |
| virtual int | GetExternalReferenceCount () const |
| for internal use only. Helps to deal with the weak-pointer-problem. | |
| void | UpdateOutputInformation () |
| Update the information for this BaseData (the geometry in particular) so that it can be used as an output of a BaseProcess. | |
| void | SetRequestedRegionToLargestPossibleRegion ()=0 |
| Set the RequestedRegion to the LargestPossibleRegion. | |
| bool | RequestedRegionIsOutsideOfTheBufferedRegion ()=0 |
| Determine whether the RequestedRegion is outside of the BufferedRegion. | |
| virtual bool | VerifyRequestedRegion ()=0 |
| Verify that the RequestedRegion is within the LargestPossibleRegion. | |
| void | CopyInformation (const itk::DataObject *data) |
| Copy information from the specified data set. | |
| virtual bool | IsInitialized () const |
| Check whether the data has been initialized, i.e., at least the Geometry and other header data has been set. | |
| virtual void | Clear () |
| Calls ClearData() and InitializeEmpty();. | |
| virtual bool | IsEmpty (unsigned int t) const |
| Check whether object contains data (at a specified time), e.g., a set of points may be empty. | |
| virtual bool | IsEmpty () const |
| Check whether object contains data (at least at one point in time), e.g., a set of points may be empty. | |
| void | SetRequestedRegion (itk::DataObject *data)=0 |
| Set the requested region from this data object to match the requested region of the data object passed in as a parameter. | |
| void | ExecuteOperation (Operation *operation) |
| overwrite if the Data can be called by an Interactor (StateMachine). | |
| virtual void | SetGeometry (Geometry3D *aGeometry3D) |
| Set the Geometry3D of the data, which will be referenced (not copied!). Assumes the data object has only 1 time step ( is a 3D object ). | |
| virtual void | SetGeometry (Geometry3D *aGeometry3D, unsigned int time) |
| Set the Geometry3D of a given time step, which will be referenced (not copied!). | |
| virtual void | SetClonedGeometry (const Geometry3D *aGeometry3D) |
| Set a clone of the provided geometry as Geometry3D of the data. Assumes the data object has only 1 time step ( is a 3D object ) | |
| virtual void | SetClonedGeometry (const Geometry3D *aGeometry3D, unsigned int time) |
| Set a clone of the provided geometry as Geometry3D of a given time step. | |
| mitk::PropertyList::Pointer | GetPropertyList () const |
| Get the data's property list. | |
| void | SetPropertyList (PropertyList *propertyList) |
| Set the data's property list. | |
| mitk::BaseProperty::Pointer | GetProperty (const char *propertyKey) const |
| Get the property (instance of BaseProperty) with key propertyKey from the PropertyList, and set it to this, respectively;. | |
| void | SetProperty (const char *propertyKey, BaseProperty *property) |
| virtual void | SetOrigin (const Point3D &origin) |
| Convenience method for setting the origin of the Geometry3D instances of all time steps. | |
| itk::SmartPointerForwardReference < mitk::BaseProcess > | GetSource () const |
| Get the process object that generated this data object. | |
| unsigned int | GetTimeSteps () const |
| Get the number of time steps from the Timeslicedgeometry As the base data has not a data vector given by itself, the number of time steps is defined over the time sliced geometry. In sub classes, a better implementation could be over the length of the data vector. | |
| virtual unsigned long | GetMTime () const |
| Get the modified time of the last change of the contents this data object or its geometry. | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| BaseData () | |
| ~BaseData () | |
| virtual void | InitializeTimeSlicedGeometry (unsigned int timeSteps=1) |
| Initialize the TimeSlicedGeometry for a number of time steps. The TimeSlicedGeometry is initialized empty and evenly timed. In many cases it will be necessary to overwrite this in sub-classes. | |
| virtual void | ClearData () |
| reset to non-initialized state, release memory | |
| virtual void | InitializeEmpty () |
| Pure virtual; Must be used in subclasses to get a data object to a valid state. Should at least create one empty object and call Superclass::InitializeTimeSlicedGeometry() to ensure an existing valid geometry. | |
| virtual void | PrintSelf (std::ostream &os, itk::Indent indent) const |
| virtual void | ConnectSource (itk::ProcessObject *arg, unsigned int idx) const |
| for internal use only. Helps to deal with the weak-pointer-problem. | |
Protected Attributes | |
| bool | m_RequestedRegionInitialized |
| bool | m_LastRequestedRegionWasOutsideOfTheBufferedRegion |
| itk::SmartPointer < mitk::BaseProcess > | m_SmartSourcePointer |
| unsigned int | m_SourceOutputIndexDuplicate |
| bool | m_Initialized |
Friends | |
| class | mitk::BaseProcess |
| Helps to deal with the weak-pointer-problem. | |
Base of all data objects.
Base of all data objects, e.g., images, contours, surfaces etc. Inherits from itk::DataObject and thus can be included in a pipeline. Inherits also from OperationActor and can be used as a destination for Undo
Definition at line 41 of file mitkBaseData.h.
| typedef itk::SmartPointer<const Self> mitk::BaseData::ConstPointer |
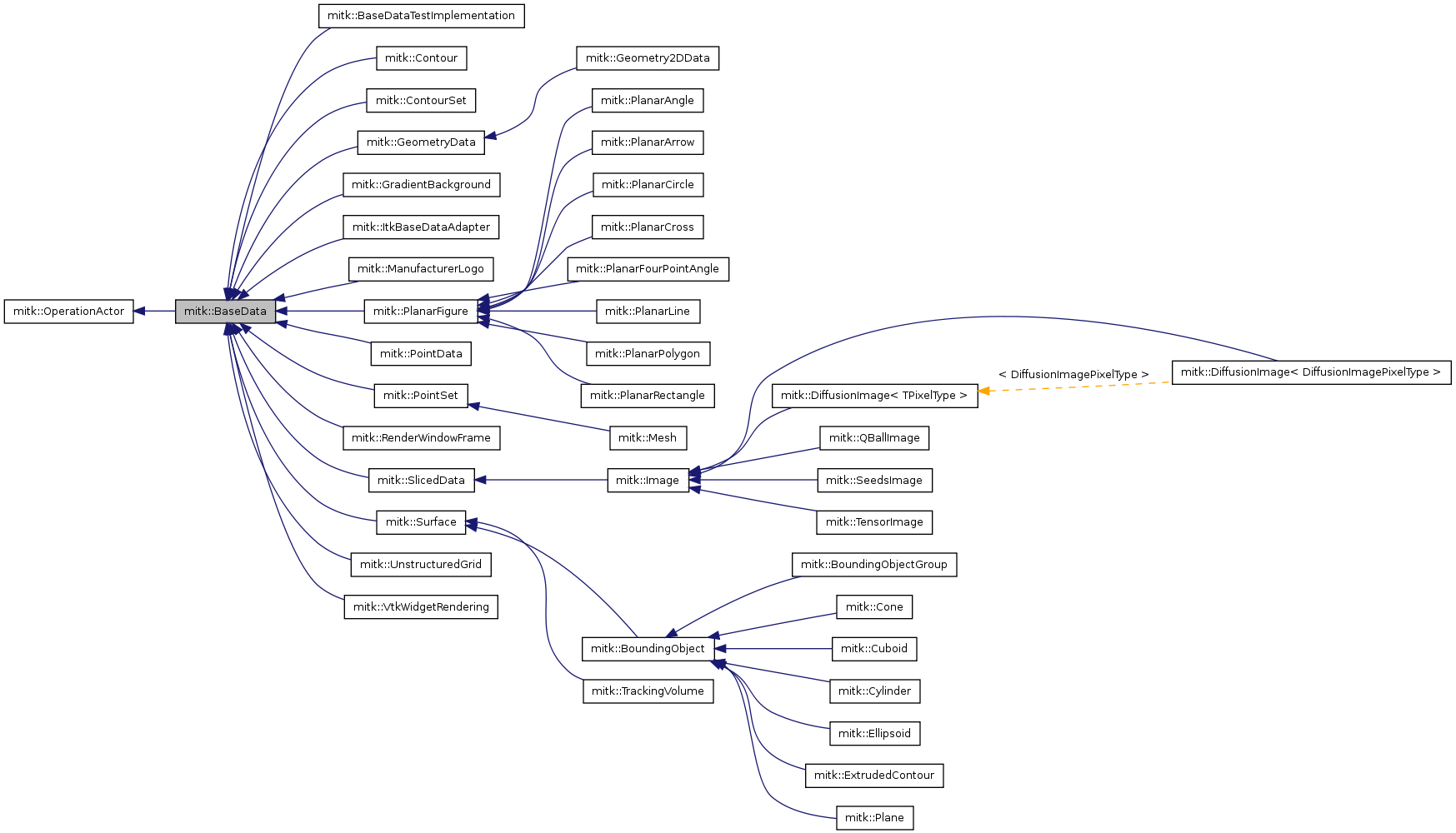
Reimplemented in mitk::BaseDataTestImplementation, mitk::Geometry2DData, mitk::GeometryData, mitk::Image, mitk::PointSet, mitk::SlicedData, mitk::Surface, mitk::GradientBackground, mitk::ManufacturerLogo, mitk::RenderWindowFrame, mitk::VtkWidgetRendering, mitk::DiffusionImage< TPixelType >, mitk::QBallImage, mitk::TensorImage, mitk::TrackingVolume, mitk::BoundingObject, mitk::BoundingObjectGroup, mitk::Cone, mitk::Contour, mitk::ContourSet, mitk::Cuboid, mitk::Cylinder, mitk::Ellipsoid, mitk::ExtrudedContour, mitk::ItkBaseDataAdapter, mitk::Mesh, mitk::Plane, mitk::PointData, mitk::SeedsImage, mitk::UnstructuredGrid, mitk::PlanarAngle, mitk::PlanarArrow, mitk::PlanarCircle, mitk::PlanarCross, mitk::PlanarFigure, mitk::PlanarFourPointAngle, mitk::PlanarLine, mitk::PlanarPolygon, mitk::PlanarRectangle, and mitk::DiffusionImage< DiffusionImagePixelType >.
Definition at line 44 of file mitkBaseData.h.
| typedef itk::SmartPointer<Self> mitk::BaseData::Pointer |
Reimplemented in mitk::BaseDataTestImplementation, mitk::Geometry2DData, mitk::GeometryData, mitk::Image, mitk::PointSet, mitk::SlicedData, mitk::Surface, mitk::GradientBackground, mitk::ManufacturerLogo, mitk::RenderWindowFrame, mitk::VtkWidgetRendering, mitk::DiffusionImage< TPixelType >, mitk::QBallImage, mitk::TensorImage, mitk::TrackingVolume, mitk::BoundingObject, mitk::BoundingObjectGroup, mitk::Cone, mitk::Contour, mitk::ContourSet, mitk::Cuboid, mitk::Cylinder, mitk::Ellipsoid, mitk::ExtrudedContour, mitk::ItkBaseDataAdapter, mitk::Mesh, mitk::Plane, mitk::PointData, mitk::SeedsImage, mitk::UnstructuredGrid, mitk::PlanarAngle, mitk::PlanarArrow, mitk::PlanarCircle, mitk::PlanarCross, mitk::PlanarFigure, mitk::PlanarFourPointAngle, mitk::PlanarLine, mitk::PlanarPolygon, mitk::PlanarRectangle, and mitk::DiffusionImage< DiffusionImagePixelType >.
Definition at line 44 of file mitkBaseData.h.
| typedef BaseData mitk::BaseData::Self |
Reimplemented in mitk::BaseDataTestImplementation, mitk::Geometry2DData, mitk::GeometryData, mitk::Image, mitk::PointSet, mitk::SlicedData, mitk::Surface, mitk::GradientBackground, mitk::ManufacturerLogo, mitk::RenderWindowFrame, mitk::VtkWidgetRendering, mitk::DiffusionImage< TPixelType >, mitk::QBallImage, mitk::TensorImage, mitk::TrackingVolume, mitk::BoundingObject, mitk::BoundingObjectGroup, mitk::Cone, mitk::Contour, mitk::ContourSet, mitk::Cuboid, mitk::Cylinder, mitk::Ellipsoid, mitk::ExtrudedContour, mitk::ItkBaseDataAdapter, mitk::Mesh, mitk::Plane, mitk::PointData, mitk::SeedsImage, mitk::UnstructuredGrid, mitk::PlanarAngle, mitk::PlanarArrow, mitk::PlanarCircle, mitk::PlanarCross, mitk::PlanarFigure, mitk::PlanarFourPointAngle, mitk::PlanarLine, mitk::PlanarPolygon, mitk::PlanarRectangle, and mitk::DiffusionImage< DiffusionImagePixelType >.
Definition at line 44 of file mitkBaseData.h.
| typedef itk::DataObject mitk::BaseData::Superclass |
Reimplemented in mitk::BaseDataTestImplementation, mitk::Geometry2DData, mitk::GeometryData, mitk::Image, mitk::PointSet, mitk::SlicedData, mitk::Surface, mitk::GradientBackground, mitk::ManufacturerLogo, mitk::RenderWindowFrame, mitk::VtkWidgetRendering, mitk::DiffusionImage< TPixelType >, mitk::QBallImage, mitk::TensorImage, mitk::TrackingVolume, mitk::BoundingObject, mitk::BoundingObjectGroup, mitk::Cone, mitk::Contour, mitk::ContourSet, mitk::Cuboid, mitk::Cylinder, mitk::Ellipsoid, mitk::ExtrudedContour, mitk::ItkBaseDataAdapter, mitk::Mesh, mitk::Plane, mitk::PointData, mitk::SeedsImage, mitk::UnstructuredGrid, mitk::PlanarAngle, mitk::PlanarArrow, mitk::PlanarCircle, mitk::PlanarCross, mitk::PlanarFigure, mitk::PlanarFourPointAngle, mitk::PlanarLine, mitk::PlanarPolygon, mitk::PlanarRectangle, and mitk::DiffusionImage< DiffusionImagePixelType >.
Definition at line 44 of file mitkBaseData.h.
| mitk::BaseData::BaseData | ( | ) | [protected] |
Definition at line 27 of file mitkBaseData.cpp.
References mitk::PropertyList::New(), and mitk::TimeSlicedGeometry::New().
: m_RequestedRegionInitialized(false), m_SmartSourcePointer(NULL), m_SourceOutputIndexDuplicate(0), m_Initialized(true), m_Unregistering(false), m_CalculatingExternalReferenceCount(false), m_ExternalReferenceCount(-1) { m_TimeSlicedGeometry = TimeSlicedGeometry::New(); m_PropertyList = PropertyList::New(); }
| mitk::BaseData::~BaseData | ( | ) | [protected] |
Definition at line 37 of file mitkBaseData.cpp.
{
m_SmartSourcePointer = NULL;
}
| void mitk::BaseData::Clear | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Calls ClearData() and InitializeEmpty();.
Reimplemented in mitk::Image.
Definition at line 326 of file mitkBaseData.cpp.
{
this->ClearData();
this->InitializeEmpty();
}
| void mitk::BaseData::ClearData | ( | ) | [protected, virtual] |
reset to non-initialized state, release memory
Reimplemented in mitk::PointSet, mitk::Surface, and mitk::UnstructuredGrid.
Definition at line 332 of file mitkBaseData.cpp.
{
if(m_Initialized)
{
ReleaseData();
m_Initialized = false;
}
}
| void mitk::BaseData::ConnectSource | ( | itk::ProcessObject * | arg, |
| unsigned int | idx | ||
| ) | const [protected, virtual] |
for internal use only. Helps to deal with the weak-pointer-problem.
Definition at line 221 of file mitkBaseData.cpp.
{
#ifdef MITK_WEAKPOINTER_PROBLEM_WORKAROUND_ENABLED
itkDebugMacro( "connecting source " << arg
<< ", source output index " << idx);
if ( GetSource() != arg || m_SourceOutputIndexDuplicate != idx)
{
m_SmartSourcePointer = dynamic_cast<mitk::BaseProcess*>(arg);
m_SourceOutputIndexDuplicate = idx;
Modified();
}
#endif
}
| void mitk::BaseData::CopyInformation | ( | const itk::DataObject * | data ) |
Copy information from the specified data set.
This method is part of the pipeline execution model. By default, a BaseProcess will copy meta-data from the first input to all of its outputs. See ProcessObject::GenerateOutputInformation(). Each subclass of DataObject is responsible for being able to copy whatever meta-data it needs from another DataObject. The default implementation of this method copies the time sliced geometry and the property list of an object. If a subclass overrides this method, it should always call its superclass' version.
Reimplemented in mitk::Geometry2DData, mitk::GeometryData, mitk::SlicedData, mitk::Surface, mitk::PointData, and mitk::UnstructuredGrid.
Definition at line 302 of file mitkBaseData.cpp.
References mitk::TimeSlicedGeometry::Clone(), GetPropertyList(), and GetTimeSlicedGeometry().
{
const Self* bd = dynamic_cast<const Self*>(data);
if (bd != NULL)
{
m_TimeSlicedGeometry = dynamic_cast<TimeSlicedGeometry*>(bd->GetTimeSlicedGeometry()->Clone().GetPointer());
m_PropertyList = bd->GetPropertyList()->Clone();
}
else
{
// pointer could not be cast back down; this can be the case if your filters input
// and output objects differ in type; then you have to write your own GenerateOutputInformation method
itkExceptionMacro(<< "mitk::BaseData::CopyInformation() cannot cast "
<< typeid(data).name() << " to "
<< typeid(Self*).name() );
}
}
| void mitk::BaseData::ExecuteOperation | ( | mitk::Operation * | operation ) | [virtual] |
overwrite if the Data can be called by an Interactor (StateMachine).
Empty by default. Overwrite and implement all the necessary operations here and get the necessary information from the parameter operation.
Implements mitk::OperationActor.
Reimplemented in mitk::PointSet, mitk::Surface, mitk::Mesh, and mitk::SeedsImage.
Definition at line 341 of file mitkBaseData.cpp.
{
//empty by default. override if needed!
}
| void mitk::BaseData::Expand | ( | unsigned int | timeSteps ) | [virtual] |
Expands the TimeSlicedGeometry to a number of TimeSteps.
The method expands the TimeSlicedGeometry to the given number of TimeSteps, filling newly created elements with empty geometries. Sub-classes should override this method to handle the elongation of their data vectors, too. Note that a shrinking is neither possible nor intended.
Reimplemented in mitk::PointSet, mitk::Surface, and mitk::UnstructuredGrid.
Definition at line 79 of file mitkBaseData.cpp.
Referenced by mitk::SurfaceDeformationInteractor3D::ExecuteAction().
{
if( m_TimeSlicedGeometry.IsNotNull() )
m_TimeSlicedGeometry->ExpandToNumberOfTimeSteps( timeSteps );
}
| virtual const char* mitk::BaseData::GetClassName | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented in mitk::BaseDataTestImplementation, mitk::Geometry2DData, mitk::GeometryData, mitk::Image, mitk::PointSet, mitk::SlicedData, mitk::Surface, mitk::GradientBackground, mitk::ManufacturerLogo, mitk::RenderWindowFrame, mitk::VtkWidgetRendering, mitk::DiffusionImage< TPixelType >, mitk::QBallImage, mitk::TensorImage, mitk::TrackingVolume, mitk::BoundingObject, mitk::BoundingObjectGroup, mitk::Cone, mitk::Contour, mitk::ContourSet, mitk::Cuboid, mitk::Cylinder, mitk::Ellipsoid, mitk::ExtrudedContour, mitk::ItkBaseDataAdapter, mitk::Mesh, mitk::Plane, mitk::PointData, mitk::SeedsImage, mitk::UnstructuredGrid, mitk::PlanarAngle, mitk::PlanarArrow, mitk::PlanarCircle, mitk::PlanarCross, mitk::PlanarFigure, mitk::PlanarFourPointAngle, mitk::PlanarLine, mitk::PlanarPolygon, mitk::PlanarRectangle, and mitk::DiffusionImage< DiffusionImagePixelType >.
| int mitk::BaseData::GetExternalReferenceCount | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
for internal use only. Helps to deal with the weak-pointer-problem.
Definition at line 159 of file mitkBaseData.cpp.
{
if(m_CalculatingExternalReferenceCount==false) //this is only needed because a smart-pointer to m_Outputs (private!!) must be created by calling GetOutputs.
{
m_CalculatingExternalReferenceCount = true;
m_ExternalReferenceCount = -1;
int realReferenceCount = GetReferenceCount();
if(GetSource()==NULL)
{
m_ExternalReferenceCount = realReferenceCount;
m_CalculatingExternalReferenceCount = false;
return m_ExternalReferenceCount;
}
mitk::BaseProcess::DataObjectPointerArray outputs = m_SmartSourcePointer->GetOutputs();
unsigned int idx;
for (idx = 0; idx < outputs.size(); ++idx)
{
//references of outputs that are not referenced from someone else (reference additional to the reference from this BaseProcess object) are interpreted as non-existent
if(outputs[idx]==this)
--realReferenceCount;
}
m_ExternalReferenceCount = realReferenceCount;
if(m_ExternalReferenceCount<0)
m_ExternalReferenceCount=0;
m_CalculatingExternalReferenceCount = false;
}
else
return -1;
return m_ExternalReferenceCount;
}
| mitk::Geometry3D* mitk::BaseData::GetGeometry | ( | int | t = 0 ) |
const [inline] |
Return the geometry, which is a TimeSlicedGeometry, of the data as non-const pointer.
Normally used in GenerateOutputInformation of subclasses of BaseProcess.
Reimplemented in mitk::BoundingObjectGroup.
Definition at line 108 of file mitkBaseData.h.
References QuadProgPP::t().
Referenced by mitk::ContourUtils::BackProjectContourFrom2DSlice(), mitk::BoundingObject::BoundingObject(), mitk::SegTool2D::DetermineAffectedImageSlice(), QmitkRegionGrowingView::DoImageProcessing(), mitk::SurfaceDeformationInteractor3D::ExecuteAction(), mitk::PlanarFigureInteractor::ExecuteAction(), QmitkImageStatistics::FillStatisticsTableView(), mitk::SurfaceIndexToWorldTransformFilter::GenerateData(), mitk::PlaneCutFilter::GenerateData(), mitk::NavigationDataObjectVisualizationFilter::GenerateData(), mitk::ExtractImageFilter::GenerateData(), mitk::BoundingObjectToSegmentationFilter::GenerateData(), MeshUtil< MeshType, ScalarAccessor >::MeshFromSurface(), mitk::PaintbrushTool::OnMouseMoved(), mitk::PlanarFigureMapper2D::Paint(), mitk::ContourUtils::ProjectContourTo2DSlice(), mitk::VolumeDataVtkMapper3D::SetClippingPlane(), mitk::CompressedImageContainer::SetImage(), testBackCasting(), testGeometryDataToSurfaceFilter(), testSurfaceBoundingBoxConsistency(), and mitk::ImageWriter::WriteByITK().
{
if(m_TimeSlicedGeometry.IsNull())
return NULL;
return m_TimeSlicedGeometry->GetGeometry3D(t);
}
| unsigned long mitk::BaseData::GetMTime | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Get the modified time of the last change of the contents this data object or its geometry.
Reimplemented in mitk::ExtrudedContour.
Definition at line 283 of file mitkBaseData.cpp.
Referenced by mitk::SimpleHistogramCache::operator[](), mitk::SplineMapper2D::Paint(), mitk::PointLocator::SetPoints(), and mitk::Mapper::Update().
{
unsigned long time = Superclass::GetMTime();
if(m_TimeSlicedGeometry.IsNotNull())
{
if((time < m_TimeSlicedGeometry->GetMTime()))
{
Modified();
return Superclass::GetMTime();
}
//unsigned long geometryTime = m_TimeSlicedGeometry->GetMTime();
//if(time < geometryTime)
//{
// return geometryTime;
//}
}
return time;
}
| mitk::BaseProperty::Pointer mitk::BaseData::GetProperty | ( | const char * | propertyKey ) | const |
Get the property (instance of BaseProperty) with key propertyKey from the PropertyList, and set it to this, respectively;.
Definition at line 242 of file mitkBaseData.cpp.
Referenced by QmitkDiffusionTensorEstimation::DirectionVolumesAngularErrorButton().
{
return m_PropertyList->GetProperty(propertyKey);
}
| mitk::PropertyList::Pointer mitk::BaseData::GetPropertyList | ( | ) | const |
Get the data's property list.
Definition at line 236 of file mitkBaseData.cpp.
Referenced by PlanarFigureIOTestClass::ComparePlanarFigures(), CopyInformation(), and mitk::SurfaceToImageFilter::GenerateOutputInformation().
{
return m_PropertyList;
}
| itk::SmartPointerForwardReference< mitk::BaseProcess > mitk::BaseData::GetSource | ( | ) | const |
Get the process object that generated this data object.
If there is no process object, then the data object has been disconnected from the pipeline, or the data object was created manually. (Note: we cannot use the GetObjectMacro() defined in itkMacro because the mutual dependency of DataObject and ProcessObject causes compile problems. Also, a forward reference smart pointer is returned, not a smart pointer, because of the circular dependency between the process and data object.)
GetSource() returns a SmartPointerForwardReference and not a WeakPointer because it is assumed the code calling GetSource() wants to hold a long term reference to the source.
Definition at line 154 of file mitkBaseData.cpp.
{
return static_cast<mitk::BaseProcess*>(Superclass::GetSource().GetPointer());
}
| const mitk::TimeSlicedGeometry* mitk::BaseData::GetTimeSlicedGeometry | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Return the TimeSlicedGeometry of the data as const pointer.
Normally used in GenerateOutputInformation of subclasses of BaseProcess.
Definition at line 53 of file mitkBaseData.h.
Referenced by mitk::BoundingObject::BoundingObject(), mitk::BoundingObjectGroup::BoundingObjectGroup(), mitk::ContourSet::ContourSet(), CopyInformation(), mitk::Tool::CreateEmptySegmentationNode(), mitk::ExtrudedContour::ExtrudedContour(), mitk::VolumeDataVtkMapper3D::GenerateData(), mitk::ProbeFilter::GenerateData(), mitk::ImageWriter::GenerateData(), mitk::ImageMapperGL2D::GenerateData(), mitk::ExtractDirectedPlaneImageFilter::GenerateData(), mitk::ProbeFilter::GenerateInputRequestedRegion(), mitk::MaskImageFilter::GenerateInputRequestedRegion(), mitk::SurfaceToImageFilter::GenerateOutputInformation(), mitk::LabeledImageToSurfaceFilter::GenerateOutputInformation(), mitk::BaseRenderer::GetTimeStep(), mitk::Image::Initialize(), mitk::SurfaceGLMapper2D::SetDataNode(), and mitk::ImageMapperGL2D::Update().
{
return m_TimeSlicedGeometry.GetPointer();
}
| mitk::TimeSlicedGeometry* mitk::BaseData::GetTimeSlicedGeometry | ( | ) | [inline] |
Return the TimeSlicedGeometry of the data as pointer.
Normally used in GenerateOutputInformation of subclasses of BaseProcess.
Definition at line 65 of file mitkBaseData.h.
{
return m_TimeSlicedGeometry.GetPointer();
}
| unsigned int mitk::BaseData::GetTimeSteps | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Get the number of time steps from the Timeslicedgeometry As the base data has not a data vector given by itself, the number of time steps is defined over the time sliced geometry. In sub classes, a better implementation could be over the length of the data vector.
Definition at line 323 of file mitkBaseData.h.
Referenced by mitk::Interactor::SetDataNode(), mitk::ImageStatisticsCalculator::SetImageMask(), mitkExtractImageFilterTestClass::Test4D(), QmitkPointListView::wheelEvent(), and mitk::PointSetWriter::WriteXML().
{
return m_TimeSlicedGeometry->GetTimeSteps();
};
| const mitk::Geometry3D * mitk::BaseData::GetUpdatedGeometry | ( | int | t = 0 ) |
Return the Geometry3D of the data at time t.
The method does not simply return m_TimeSlicedGeometry->GetGeometry(t). Before doing this, it makes sure that the Geometry3D is up-to-date (by setting the update extent appropriately and calling UpdateOutputInformation).
Definition at line 85 of file mitkBaseData.cpp.
{
SetRequestedRegionToLargestPossibleRegion();
UpdateOutputInformation();
return GetGeometry(t);
}
| const mitk::TimeSlicedGeometry * mitk::BaseData::GetUpdatedTimeSlicedGeometry | ( | ) |
Return the Geometry3D of the data.
The method does not simply return the value of the m_TimeSlicedGeometry member. Before doing this, it makes sure that the TimeSlicedGeometry is up-to-date (by setting the update extent to largest possible and calling UpdateOutputInformation).
Definition at line 70 of file mitkBaseData.cpp.
Referenced by mitk::MoveSurfaceInteractor::ExecuteAction(), and mitk::VectorImageMapper2D::GetCurrentTimeStep().
{
SetRequestedRegionToLargestPossibleRegion();
UpdateOutputInformation();
return GetTimeSlicedGeometry();
}
| virtual void mitk::BaseData::InitializeEmpty | ( | ) | [inline, protected, virtual] |
Pure virtual; Must be used in subclasses to get a data object to a valid state. Should at least create one empty object and call Superclass::InitializeTimeSlicedGeometry() to ensure an existing valid geometry.
Reimplemented in mitk::PointSet, mitk::Surface, and mitk::UnstructuredGrid.
Definition at line 352 of file mitkBaseData.h.
{};
| void mitk::BaseData::InitializeTimeSlicedGeometry | ( | unsigned int | timeSteps = 1 ) |
[protected, virtual] |
Initialize the TimeSlicedGeometry for a number of time steps. The TimeSlicedGeometry is initialized empty and evenly timed. In many cases it will be necessary to overwrite this in sub-classes.
Reimplemented in mitk::BaseDataTestImplementation, and mitk::PlanarFigure.
Definition at line 42 of file mitkBaseData.cpp.
References mitk::Geometry3D::New().
Referenced by mitk::Contour::Contour(), and mitk::BaseDataTestImplementation::InitializeTimeSlicedGeometry().
{
mitk::TimeSlicedGeometry::Pointer timeGeometry = this->GetTimeSlicedGeometry();
mitk::Geometry3D::Pointer g3d = mitk::Geometry3D::New();
g3d->Initialize();
if ( timeSteps > 1 )
{
mitk::ScalarType timeBounds[] = {0.0, 1.0};
g3d->SetTimeBounds( timeBounds );
}
// The geometry is propagated automatically to the other items,
// if EvenlyTimed is true...
timeGeometry->InitializeEvenlyTimed( g3d.GetPointer(), timeSteps );
}
| bool mitk::BaseData::IsEmpty | ( | unsigned int | t ) | const [virtual] |
Check whether object contains data (at a specified time), e.g., a set of points may be empty.
Reimplemented in mitk::PointSet, and mitk::Surface.
Definition at line 133 of file mitkBaseData.cpp.
{
return IsInitialized() == false;
}
| bool mitk::BaseData::IsEmpty | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Check whether object contains data (at least at one point in time), e.g., a set of points may be empty.
Definition at line 138 of file mitkBaseData.cpp.
References mitk::TimeSlicedGeometry::GetTimeSteps(), and QuadProgPP::t().
{
if(IsInitialized() == false)
return true;
const TimeSlicedGeometry* timeGeometry = const_cast<BaseData*>(this)->GetUpdatedTimeSlicedGeometry();
if(timeGeometry == NULL)
return true;
unsigned int timeSteps = timeGeometry->GetTimeSteps();
for ( unsigned int t = 0 ; t < timeSteps ; ++t )
{
if(IsEmpty(t) == false)
return false;
}
return true;
}
| bool mitk::BaseData::IsInitialized | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Check whether the data has been initialized, i.e., at least the Geometry and other header data has been set.
Definition at line 321 of file mitkBaseData.cpp.
Referenced by mitk::VolumeDataVtkMapper3D::GenerateData(), mitk::SurfaceToImageFilter::GenerateInputRequestedRegion(), mitk::RGBToRGBACastImageFilter::GenerateInputRequestedRegion(), mitk::MaskImageFilter::GenerateInputRequestedRegion(), mitk::GeometryClipImageFilter::GenerateInputRequestedRegion(), mitk::SurfaceToImageFilter::GenerateOutputInformation(), mitk::HeightFieldSurfaceClipImageFilter::GenerateOutputInformation(), mitk::BaseRenderer::GetTimeStep(), mitk::GPUVolumeMapper3D::IsRenderable(), QmitkVolumetryView::OnImageSelected(), and mitk::LevelWindow::SetAuto().
{
return m_Initialized;
}
| void mitk::BaseData::PrintSelf | ( | std::ostream & | os, |
| itk::Indent | indent | ||
| ) | const [protected, virtual] |
Reimplemented in mitk::Image, mitk::PointSet, mitk::Surface, mitk::Contour, mitk::ItkBaseDataAdapter, mitk::PlanarAngle, mitk::PlanarArrow, mitk::PlanarCircle, mitk::PlanarCross, mitk::PlanarFigure, mitk::PlanarFourPointAngle, mitk::PlanarLine, mitk::PlanarPolygon, and mitk::PlanarRectangle.
Definition at line 346 of file mitkBaseData.cpp.
{
os << std::endl;
os << indent << " TimeSlicedGeometry: ";
if(GetTimeSlicedGeometry() == NULL)
os << "NULL" << std::endl;
else
GetTimeSlicedGeometry()->Print(os, indent);
}
| bool mitk::BaseData::RequestedRegionIsOutsideOfTheBufferedRegion | ( | ) | [pure virtual] |
Determine whether the RequestedRegion is outside of the BufferedRegion.
This method returns true if the RequestedRegion is outside the BufferedRegion (true if at least one pixel is outside). This is used by the pipeline mechanism to determine whether a filter needs to re-execute in order to satisfy the current request. If the current RequestedRegion is already inside the BufferedRegion from the previous execution (and the current filter is up to date), then a given filter does not need to re-execute
Implemented in mitk::BaseDataTestImplementation, mitk::Geometry2DData, mitk::GeometryData, mitk::PointSet, mitk::SlicedData, mitk::Surface, mitk::GradientBackground, mitk::ManufacturerLogo, mitk::RenderWindowFrame, mitk::VtkWidgetRendering, mitk::Contour, mitk::ContourSet, mitk::ItkBaseDataAdapter, mitk::PointData, mitk::UnstructuredGrid, and mitk::PlanarFigure.
| void mitk::BaseData::SetClonedGeometry | ( | const Geometry3D * | aGeometry3D ) | [virtual] |
Set a clone of the provided geometry as Geometry3D of the data. Assumes the data object has only 1 time step ( is a 3D object )
Definition at line 123 of file mitkBaseData.cpp.
References mitk::Geometry3D::Clone().
{
SetGeometry(static_cast<mitk::Geometry3D*>(aGeometry3D->Clone().GetPointer()));
}
| void mitk::BaseData::SetClonedGeometry | ( | const Geometry3D * | aGeometry3D, |
| unsigned int | time | ||
| ) | [virtual] |
Set a clone of the provided geometry as Geometry3D of a given time step.
Definition at line 128 of file mitkBaseData.cpp.
References mitk::Geometry3D::Clone().
{
SetGeometry(static_cast<mitk::Geometry3D*>(aGeometry3D->Clone().GetPointer()), time);
}
| void mitk::BaseData::SetGeometry | ( | Geometry3D * | aGeometry3D ) | [virtual] |
Set the Geometry3D of the data, which will be referenced (not copied!). Assumes the data object has only 1 time step ( is a 3D object ).
For convenience (and historic) reasons, it is also possible to set a complete mitk::TimeSlicedGeometry*, which will be referenced (not copied!).
Reimplemented in mitk::Geometry2DData, mitk::Image, and mitk::SlicedData.
Definition at line 94 of file mitkBaseData.cpp.
References mitk::TimeSlicedGeometry::New().
{
if(aGeometry3D!=NULL)
{
TimeSlicedGeometry::Pointer timeSlicedGeometry = dynamic_cast<TimeSlicedGeometry*>(aGeometry3D);
if ( timeSlicedGeometry.IsNotNull() )
m_TimeSlicedGeometry = timeSlicedGeometry;
else
{
timeSlicedGeometry = TimeSlicedGeometry::New();
m_TimeSlicedGeometry = timeSlicedGeometry;
timeSlicedGeometry->InitializeEvenlyTimed(aGeometry3D, 1);
}
Modified();
}
else if( m_TimeSlicedGeometry.IsNotNull() )
{
m_TimeSlicedGeometry = NULL;
Modified();
}
return;
}
| void mitk::BaseData::SetGeometry | ( | Geometry3D * | aGeometry3D, |
| unsigned int | time | ||
| ) | [virtual] |
Set the Geometry3D of a given time step, which will be referenced (not copied!).
Definition at line 117 of file mitkBaseData.cpp.
{
if ( m_TimeSlicedGeometry )
m_TimeSlicedGeometry->SetGeometry3D(aGeometry3D, time);
}
| virtual void mitk::BaseData::SetOrigin | ( | const Point3D & | origin ) | [virtual] |
Convenience method for setting the origin of the Geometry3D instances of all time steps.
Reimplemented in mitk::SlicedData.
| void mitk::BaseData::SetProperty | ( | const char * | propertyKey, |
| BaseProperty * | property | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 247 of file mitkBaseData.cpp.
Referenced by main(), mitk::PlanarCircle::PlanarCircle(), mitk::PlanarCross::PlanarCross(), mitk::PlanarFigure::PlanarFigure(), mitk::PlanarPolygon::PlanarPolygon(), and mitk::PlanarRectangle::PlanarRectangle().
{
m_PropertyList->SetProperty(propertyKey, propertyValue);
}
| void mitk::BaseData::SetPropertyList | ( | PropertyList * | propertyList ) |
Set the data's property list.
Definition at line 253 of file mitkBaseData.cpp.
{
m_PropertyList = pList;
}
| void mitk::BaseData::SetRequestedRegion | ( | itk::DataObject * | data ) | [pure virtual] |
Set the requested region from this data object to match the requested region of the data object passed in as a parameter.
This method is implemented in the concrete subclasses of BaseData.
Implemented in mitk::BaseDataTestImplementation, mitk::Geometry2DData, mitk::GeometryData, mitk::PointSet, mitk::SlicedData, mitk::Surface, mitk::GradientBackground, mitk::ManufacturerLogo, mitk::RenderWindowFrame, mitk::VtkWidgetRendering, mitk::Contour, mitk::ContourSet, mitk::ItkBaseDataAdapter, mitk::PointData, mitk::UnstructuredGrid, and mitk::PlanarFigure.
| void mitk::BaseData::SetRequestedRegionToLargestPossibleRegion | ( | ) | [pure virtual] |
Set the RequestedRegion to the LargestPossibleRegion.
This forces a filter to produce all of the output in one execution (i.e. not streaming) on the next call to Update().
Implemented in mitk::BaseDataTestImplementation, mitk::Geometry2DData, mitk::GeometryData, mitk::PointSet, mitk::SlicedData, mitk::Surface, mitk::GradientBackground, mitk::ManufacturerLogo, mitk::RenderWindowFrame, mitk::VtkWidgetRendering, mitk::Contour, mitk::ContourSet, mitk::ItkBaseDataAdapter, mitk::PointData, mitk::UnstructuredGrid, and mitk::PlanarFigure.
| void mitk::BaseData::UnRegister | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Helps to deal with the weak-pointer-problem.
Definition at line 195 of file mitkBaseData.cpp.
{
#ifdef MITK_WEAKPOINTER_PROBLEM_WORKAROUND_ENABLED
if(GetReferenceCount()>1)
{
Superclass::UnRegister();
if((m_Unregistering==false) && (m_SmartSourcePointer.IsNotNull()))
{
m_Unregistering=true;
// the order of the following boolean statement is important:
// this->GetSource() returns a SmartPointerForwardReference,
// which increases and afterwards decreases the reference count,
// which may result in an ExternalReferenceCount of 0, causing
// BaseProcess::UnRegister() to destroy us (also we already
// about to do that).
if((this->m_SmartSourcePointer->GetExternalReferenceCount()==0) || (this->GetSource()==NULL))
m_SmartSourcePointer=NULL; // now the reference count is zero and this object has been destroyed; thus nothing may be done after this line!!
else
m_Unregistering=false;
}
}
else
#endif
Superclass::UnRegister(); // now the reference count is zero and this object has been destroyed; thus nothing may be done after this line!!
}
| void mitk::BaseData::UpdateOutputInformation | ( | ) |
Update the information for this BaseData (the geometry in particular) so that it can be used as an output of a BaseProcess.
This method is used in the pipeline mechanism to propagate information and initialize the meta data associated with a BaseData. Any implementation of this method in a derived class is assumed to call its source's BaseProcess::UpdateOutputInformation() which determines modified times, LargestPossibleRegions, and any extra meta data like spacing, origin, etc. Default implementation simply call's it's source's UpdateOutputInformation().
Reimplemented in mitk::Geometry2DData, mitk::GeometryData, mitk::PointSet, mitk::SlicedData, mitk::Surface, mitk::BoundingObjectGroup, mitk::Contour, mitk::ContourSet, mitk::ExtrudedContour, mitk::PointData, mitk::UnstructuredGrid, and mitk::PlanarFigure.
Definition at line 60 of file mitkBaseData.cpp.
Referenced by mitk::SurfaceDeformationInteractor3D::ExecuteAction().
| virtual bool mitk::BaseData::VerifyRequestedRegion | ( | ) | [pure virtual] |
Verify that the RequestedRegion is within the LargestPossibleRegion.
If the RequestedRegion is not within the LargestPossibleRegion, then the filter cannot possibly satisfy the request. This method returns true if the request can be satisfied (even if it will be necessary to process the entire LargestPossibleRegion) and returns false otherwise. This method is used by PropagateRequestedRegion(). PropagateRequestedRegion() throws a InvalidRequestedRegionError exception if the requested region is not within the LargestPossibleRegion.
Implemented in mitk::BaseDataTestImplementation, mitk::Geometry2DData, mitk::GeometryData, mitk::PointSet, mitk::SlicedData, mitk::Surface, mitk::GradientBackground, mitk::ManufacturerLogo, mitk::RenderWindowFrame, mitk::VtkWidgetRendering, mitk::BoundingObjectGroup, mitk::Contour, mitk::ContourSet, mitk::ItkBaseDataAdapter, mitk::PointData, mitk::UnstructuredGrid, and mitk::PlanarFigure.
friend class mitk::BaseProcess [friend] |
Helps to deal with the weak-pointer-problem.
Definition at line 389 of file mitkBaseData.h.
bool mitk::BaseData::m_Initialized [protected] |
Definition at line 367 of file mitkBaseData.h.
Referenced by mitk::Image::Image().
bool mitk::BaseData::m_LastRequestedRegionWasOutsideOfTheBufferedRegion [protected] |
Definition at line 358 of file mitkBaseData.h.
bool mitk::BaseData::m_RequestedRegionInitialized [protected] |
Definition at line 357 of file mitkBaseData.h.
itk::SmartPointer<mitk::BaseProcess> mitk::BaseData::m_SmartSourcePointer [mutable, protected] |
Definition at line 360 of file mitkBaseData.h.
unsigned int mitk::BaseData::m_SourceOutputIndexDuplicate [mutable, protected] |
Definition at line 361 of file mitkBaseData.h.
 1.7.2
1.7.2