Superclass of all classes generating Images (instances of class Image) as output. More...
#include <mitkImageSource.h>
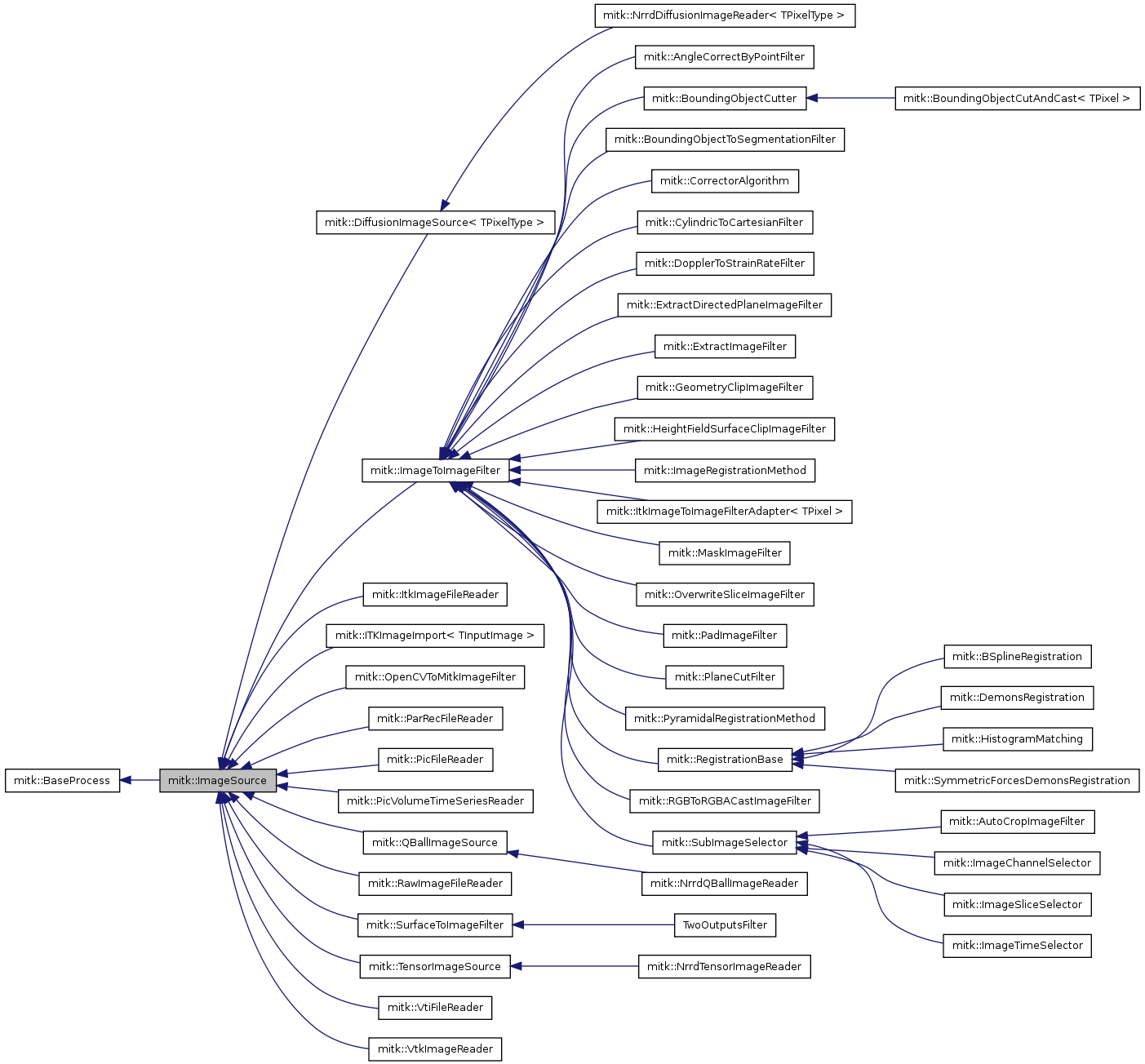
Classes | |
| struct | ThreadStruct |
| Internal structure used for passing image data into the threading library. More... | |
Public Types | |
| typedef itk::DataObject::Pointer | DataObjectPointer |
| Smart Pointer type to a DataObject. | |
| typedef mitk::Image | OutputImageType |
| Some convenient typedefs. | |
| typedef OutputImageType::Pointer | OutputImagePointer |
| typedef SlicedData::RegionType | OutputImageRegionType |
Public Member Functions | |
| mitkClassMacro (ImageSource, BaseProcess) | |
| OutputImageType * | GetOutput (void) |
| Get the image output of this process object. | |
| OutputImageType * | GetOutput (unsigned int idx) |
| void | SetOutput (OutputImageType *output) |
| Set the image output of this process object. | |
| virtual void | GraftOutput (OutputImageType *output) |
| Graft the specified DataObject onto this ProcessObject's output. | |
| virtual void | GraftNthOutput (unsigned int idx, OutputImageType *output) |
| Graft the specified data object onto this ProcessObject's idx'th output. | |
| virtual DataObjectPointer | MakeOutput (unsigned int idx) |
| Make a DataObject of the correct type to used as the specified output. | |
| virtual void * | GetData () |
| virtual mitkIpPicDescriptor * | GetPic () |
| virtual vtkImageData * | GetVtkImageData () |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static Pointer | New () |
| Method for creation through the object factory. | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| ImageSource () | |
| virtual | ~ImageSource () |
| virtual void | GenerateData () |
| A version of GenerateData() specific for image processing filters. | |
| virtual void | ThreadedGenerateData (const OutputImageRegionType &outputRegionForThread, int threadId) |
| If an imaging filter can be implemented as a multithreaded algorithm, the filter will provide an implementation of ThreadedGenerateData(). | |
| virtual void | PrepareOutputs () |
| This method is intentionally left blank. | |
| virtual void | AllocateOutputs () |
| The GenerateData method normally allocates the buffers for all of the outputs of a filter. | |
| virtual void | BeforeThreadedGenerateData () |
| If an imaging filter needs to perform processing after the buffer has been allocated but before threads are spawned, the filter can can provide an implementation for BeforeThreadedGenerateData(). | |
| virtual void | AfterThreadedGenerateData () |
| If an imaging filter needs to perform processing after all processing threads have completed, the filter can can provide an implementation for AfterThreadedGenerateData(). | |
| virtual int | SplitRequestedRegion (int i, int num, OutputImageRegionType &splitRegion) |
| Split the output's RequestedRegion into "num" pieces, returning region "i" as "splitRegion". | |
Static Protected Member Functions | |
| static ITK_THREAD_RETURN_TYPE | ThreaderCallback (void *arg) |
| Static function used as a "callback" by the MultiThreader. | |
Superclass of all classes generating Images (instances of class Image) as output.
In itk and vtk the generated result of a ProcessObject is only guaranteed to be up-to-date, when Update() of the ProcessObject or the generated DataObject is called immediately before access of the data stored in the DataObject. This is also true for subclasses of mitk::BaseProcess and thus for mitk::ImageSource. But there are also three access methods provided that guarantee an up-to-date result (by first calling Update and then returning the result of GetOutput()): GetData(), GetPic() and GetVtkImageData().
Definition at line 41 of file mitkImageSource.h.
| typedef itk::DataObject::Pointer mitk::ImageSource::DataObjectPointer |
Smart Pointer type to a DataObject.
Reimplemented in mitk::DiffusionImageSource< TPixelType >, mitk::QBallImageSource, and mitk::TensorImageSource.
Definition at line 47 of file mitkImageSource.h.
Reimplemented in mitk::QBallImageSource, and mitk::TensorImageSource.
Definition at line 54 of file mitkImageSource.h.
Reimplemented in mitk::ImageToImageFilter, mitk::QBallImageSource, and mitk::TensorImageSource.
Definition at line 55 of file mitkImageSource.h.
Some convenient typedefs.
Reimplemented in mitk::QBallImageSource, and mitk::TensorImageSource.
Definition at line 50 of file mitkImageSource.h.
| mitk::ImageSource::ImageSource | ( | ) | [protected] |
Definition at line 21 of file mitkImageSource.cpp.
References MakeOutput(), and mitk::BaseProcess::SetNthOutput().
{
// Create the output. We use static_cast<> here because we know the default
// output must be of type TOutputImage
OutputImageType::Pointer output
= static_cast<OutputImageType*>(this->MakeOutput(0).GetPointer());
Superclass::SetNumberOfRequiredOutputs(1);
Superclass::SetNthOutput(0, output.GetPointer());
}
| virtual mitk::ImageSource::~ImageSource | ( | ) | [inline, protected, virtual] |
Definition at line 140 of file mitkImageSource.h.
{}
| virtual void mitk::ImageSource::AfterThreadedGenerateData | ( | ) | [inline, protected, virtual] |
If an imaging filter needs to perform processing after all processing threads have completed, the filter can can provide an implementation for AfterThreadedGenerateData().
The execution flow in the default GenerateData() method will be: 1) Allocate the output buffer 2) Call BeforeThreadedGenerateData() 3) Spawn threads, calling ThreadedGenerateData() in each thread. 4) Call AfterThreadedGenerateData() Note that this flow of control is only available if a filter provides a ThreadedGenerateData() method and NOT a GenerateData() method.
Definition at line 233 of file mitkImageSource.h.
{};
| void mitk::ImageSource::AllocateOutputs | ( | ) | [protected, virtual] |
The GenerateData method normally allocates the buffers for all of the outputs of a filter.
Some filters may want to override this default behavior. For example, a filter may have multiple outputs with varying resolution. Or a filter may want to process data in place by grafting its input to its output.
Definition at line 168 of file mitkImageSource.cpp.
{
OutputImagePointer outputPtr;
// Allocate the output memory
for (unsigned int i=0; i < this->GetNumberOfOutputs(); i++)
{
outputPtr = this->GetOutput(i);
// outputPtr->SetBufferedRegion(outputPtr->GetRequestedRegion()); @FIXME???
// outputPtr->Allocate(); @FIXME???
}
}
| virtual void mitk::ImageSource::BeforeThreadedGenerateData | ( | ) | [inline, protected, virtual] |
If an imaging filter needs to perform processing after the buffer has been allocated but before threads are spawned, the filter can can provide an implementation for BeforeThreadedGenerateData().
The execution flow in the default GenerateData() method will be: 1) Allocate the output buffer 2) Call BeforeThreadedGenerateData() 3) Spawn threads, calling ThreadedGenerateData() in each thread. 4) Call AfterThreadedGenerateData() Note that this flow of control is only available if a filter provides a ThreadedGenerateData() method and NOT a GenerateData() method.
Definition at line 219 of file mitkImageSource.h.
{};
| void mitk::ImageSource::GenerateData | ( | ) | [protected, virtual] |
A version of GenerateData() specific for image processing filters.
This implementation will split the processing across multiple threads. The buffer is allocated by this method. Then the BeforeThreadedGenerateData() method is called (if provided). Then, a series of threads are spawned each calling ThreadedGenerateData(). After all the threads have completed processing, the AfterThreadedGenerateData() method is called (if provided). If an image processing filter cannot be threaded, the filter should provide an implementation of GenerateData(). That implementation is responsible for allocating the output buffer. If a filter an be threaded, it should NOT provide a GenerateData() method but should provide a ThreadedGenerateData() instead.
Reimplemented in mitk::ImageChannelSelector, mitk::ImageSliceSelector, mitk::ImageTimeSelector, mitk::ITKImageImport< TInputImage >, mitk::RGBToRGBACastImageFilter, mitk::ItkImageFileReader, mitk::PicFileReader, mitk::PicVolumeTimeSeriesReader, mitk::RawImageFileReader, mitk::VtiFileReader, mitk::VtkImageReader, mitk::BSplineRegistration, mitk::DemonsRegistration, mitk::HistogramMatching, mitk::SymmetricForcesDemonsRegistration, mitk::NrrdDiffusionImageReader< TPixelType >, mitk::NrrdQBallImageReader, mitk::NrrdTensorImageReader, mitk::AngleCorrectByPointFilter, mitk::AutoCropImageFilter, mitk::BoundingObjectCutter, mitk::BoundingObjectToSegmentationFilter, mitk::CorrectorAlgorithm, mitk::CylindricToCartesianFilter, mitk::DopplerToStrainRateFilter, mitk::ExtractDirectedPlaneImageFilter, mitk::ExtractImageFilter, mitk::GeometryClipImageFilter, mitk::HeightFieldSurfaceClipImageFilter, mitk::ItkImageToImageFilterAdapter< TPixel >, mitk::MaskImageFilter, mitk::OverwriteSliceImageFilter, mitk::PadImageFilter, mitk::PlaneCutFilter, mitk::SurfaceToImageFilter, mitk::ParRecFileReader, mitk::OpenCVToMitkImageFilter, mitk::ImageRegistrationMethod, and mitk::PyramidalRegistrationMethod.
Definition at line 183 of file mitkImageSource.cpp.
References mitk::ImageSource::ThreadStruct::Filter.
{
// Call a method that can be overriden by a subclass to allocate
// memory for the filter's outputs
this->AllocateOutputs();
// Call a method that can be overridden by a subclass to perform
// some calculations prior to splitting the main computations into
// separate threads
this->BeforeThreadedGenerateData();
// Set up the multithreaded processing
ThreadStruct str;
str.Filter = this;
this->GetMultiThreader()->SetNumberOfThreads(this->GetNumberOfThreads());
this->GetMultiThreader()->SetSingleMethod(this->ThreaderCallback, &str);
// multithread the execution
this->GetMultiThreader()->SingleMethodExecute();
// Call a method that can be overridden by a subclass to perform
// some calculations after all the threads have completed
this->AfterThreadedGenerateData();
}
| void * mitk::ImageSource::GetData | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Definition at line 257 of file mitkImageSource.cpp.
| mitk::ImageSource::OutputImageType * mitk::ImageSource::GetOutput | ( | void | ) |
Get the image output of this process object.
Definition at line 42 of file mitkImageSource.cpp.
Referenced by mitk::Image::ComputeImageStatistics(), mitk::PlaneCutFilter::GenerateData(), mitk::ItkImageFileReader::GenerateData(), mitk::ExtractImageFilter::GenerateData(), mitk::SymmetricForcesDemonsRegistration::GenerateData2(), mitk::HistogramMatching::GenerateData2(), mitk::DemonsRegistration::GenerateData2(), mitk::PicVolumeTimeSeriesReader::GenerateOutputInformation(), mitk::PicFileReader::GenerateOutputInformation(), mitk::ParRecFileReader::GenerateOutputInformation(), mitk::ImageSliceSelector::GenerateOutputInformation(), mitk::HeightFieldSurfaceClipImageFilter::GenerateOutputInformation(), mitk::DopplerToStrainRateFilter::GenerateOutputInformation(), mitk::Image::GetScalarHistogram(), mitk::ImportItkImage(), mitk::ExtractImageFilter::ItkImageProcessing(), mitkExtractImageFilterTestClass::Test2D(), mitkOverwriteSliceImageFilterTestClass::Test3D(), mitkExtractImageFilterTestClass::Test3D(), and mitkExtractImageFilterTestClass::Test4D().
{
if (this->GetNumberOfOutputs() < 1)
{
return 0;
}
return static_cast<OutputImageType*>
(this->BaseProcess::GetOutput(0));
}
| mitk::ImageSource::OutputImageType * mitk::ImageSource::GetOutput | ( | unsigned int | idx ) |
Reimplemented in mitk::OpenCVToMitkImageFilter.
Definition at line 57 of file mitkImageSource.cpp.
{
return static_cast<OutputImageType*>
(this->ProcessObject::GetOutput(idx));
}
| mitkIpPicDescriptor * mitk::ImageSource::GetPic | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Definition at line 263 of file mitkImageSource.cpp.
| vtkImageData * mitk::ImageSource::GetVtkImageData | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Definition at line 269 of file mitkImageSource.cpp.
{
Update();
return GetOutput()->GetVtkImageData();
}
| void mitk::ImageSource::GraftNthOutput | ( | unsigned int | idx, |
| OutputImageType * | output | ||
| ) | [virtual] |
Graft the specified data object onto this ProcessObject's idx'th output.
This is the similar to GraftOutput method except is allows you specify which output is affected. The specified index must be a valid output number (less than ProcessObject::GetNumberOfOutputs()). See the GraftOutput for general usage information.
Definition at line 86 of file mitkImageSource.cpp.
References mitk::SlicedData::CopyInformation(), and mitk::SlicedData::SetRequestedRegion().
{
itkWarningMacro(<< "GraftNthOutput(): This method is not yet implemented for mitk. Implement it before using!!" );
assert(false);
if (idx < this->GetNumberOfOutputs())
{
OutputImageType * output = this->GetOutput(idx);
if (output && graft)
{
// grab a handle to the bulk data of the specified data object
// output->SetPixelContainer( graft->GetPixelContainer() ); @FIXME!!!!
// copy the region ivars of the specified data object
output->SetRequestedRegion( graft );//graft->GetRequestedRegion() );
// output->SetLargestPossibleRegion( graft->GetLargestPossibleRegion() ); @FIXME!!!!
// output->SetBufferedRegion( graft->GetBufferedRegion() ); @FIXME!!!!
// copy the meta-information
output->CopyInformation( graft );
}
}
}
| void mitk::ImageSource::GraftOutput | ( | OutputImageType * | output ) | [virtual] |
Graft the specified DataObject onto this ProcessObject's output.
This method grabs a handle to the specified DataObject's bulk data to used as its output's own bulk data. It also copies the region ivars (RequestedRegion, BufferedRegion, LargestPossibleRegion) and meta-data (Spacing, Origin) from the specified data object into this filter's output data object. Most importantly, however, it leaves the Source ivar untouched so the original pipeline routing is intact. This method is used when a process object is implemented using a mini-pipeline which is defined in its GenerateData() method. The usage is:
// setup the mini-pipeline to process the input to this filter firstFilterInMiniPipeline->SetInput( this->GetInput() ); // setup the mini-pipeline to calculate the correct regions // and write to the appropriate bulk data block lastFilterInMiniPipeline->GraftOutput( this->GetOutput() ); // execute the mini-pipeline lastFilterInMiniPipeline->Update(); // graft the mini-pipeline output back onto this filter's output. // this is needed to get the appropriate regions passed back. this->GraftOutput( lastFilterInMiniPipeline->GetOutput() );
For proper pipeline execution, a filter using a mini-pipeline must implement the GenerateInputRequestedRegion(), GenerateOutputRequestedRegion(), GenerateOutputInformation() and EnlargeOutputRequestedRegion() methods as necessary to reflect how the mini-pipeline will execute (in other words, the outer filter's pipeline mechanism must be consistent with what the mini-pipeline will do).
Definition at line 77 of file mitkImageSource.cpp.
{
this->GraftNthOutput(0, graft);
}
| mitk::ImageSource::DataObjectPointer mitk::ImageSource::MakeOutput | ( | unsigned int | idx ) | [virtual] |
Make a DataObject of the correct type to used as the specified output.
Every ProcessObject subclass must be able to create a DataObject that can be used as a specified output. This method is automatically called when DataObject::DisconnectPipeline() is called. DataObject::DisconnectPipeline, disconnects a data object from being an output of its current source. When the data object is disconnected, the ProcessObject needs to construct a replacement output data object so that the ProcessObject is in a valid state. So DataObject::DisconnectPipeline eventually calls ProcessObject::MakeOutput. Note that MakeOutput always returns a SmartPointer to a DataObject. If a subclass of ImageSource has multiple outputs of different types, then that class must provide an implementation of MakeOutput().
Reimplemented in mitk::DiffusionImageSource< TPixelType >, mitk::QBallImageSource, mitk::TensorImageSource, and mitk::OpenCVToMitkImageFilter.
Definition at line 34 of file mitkImageSource.cpp.
Referenced by ImageSource(), and TwoOutputsFilter::TwoOutputsFilter().
{
return static_cast<itk::DataObject*>(OutputImageType::New().GetPointer());
}
| mitk::ImageSource::mitkClassMacro | ( | ImageSource | , |
| BaseProcess | |||
| ) |
| static Pointer mitk::ImageSource::New | ( | ) | [static] |
Method for creation through the object factory.
Reimplemented in mitk::ImageChannelSelector, mitk::ImageSliceSelector, mitk::ImageTimeSelector, mitk::ImageToImageFilter, mitk::ITKImageImport< TInputImage >, mitk::RGBToRGBACastImageFilter, mitk::SubImageSelector, mitk::ItkImageFileReader, mitk::PicFileReader, mitk::PicVolumeTimeSeriesReader, mitk::RawImageFileReader, mitk::VtiFileReader, mitk::VtkImageReader, mitk::BSplineRegistration, mitk::DemonsRegistration, mitk::HistogramMatching, mitk::RegistrationBase, mitk::SymmetricForcesDemonsRegistration, mitk::DiffusionImageSource< TPixelType >, mitk::NrrdDiffusionImageReader< TPixelType >, mitk::NrrdQBallImageReader, mitk::QBallImageSource, mitk::NrrdTensorImageReader, mitk::TensorImageSource, mitk::AngleCorrectByPointFilter, mitk::AutoCropImageFilter, mitk::BoundingObjectCutAndCast< TPixel >, mitk::BoundingObjectCutter, mitk::BoundingObjectToSegmentationFilter, mitk::CorrectorAlgorithm, mitk::CylindricToCartesianFilter, mitk::DopplerToStrainRateFilter, mitk::ExtractDirectedPlaneImageFilter, mitk::ExtractImageFilter, mitk::GeometryClipImageFilter, mitk::HeightFieldSurfaceClipImageFilter, mitk::ItkImageToImageFilterAdapter< TPixel >, mitk::MaskImageFilter, mitk::OverwriteSliceImageFilter, mitk::PadImageFilter, mitk::PlaneCutFilter, mitk::SurfaceToImageFilter, mitk::ParRecFileReader, TwoOutputsFilter, mitk::OpenCVToMitkImageFilter, mitk::ImageRegistrationMethod, and mitk::PyramidalRegistrationMethod.
| void mitk::ImageSource::PrepareOutputs | ( | ) | [protected, virtual] |
This method is intentionally left blank.
ImageSource's need not Initialize their containers. The Image::Allocate() method (called from GenerateData()) will resize the container if more memory is needed. Otherwise, the memory can be reused.
Definition at line 252 of file mitkImageSource.cpp.
{
Superclass::PrepareOutputs();
}
| void mitk::ImageSource::SetOutput | ( | OutputImageType * | output ) |
Set the image output of this process object.
This call is slated to be removed from ITK. You should GraftOutput() and possible DataObject::DisconnectPipeline() to properly change the output.
Definition at line 67 of file mitkImageSource.cpp.
References mitk::BaseProcess::SetNthOutput().
{
itkWarningMacro(<< "SetOutput(): This method is slated to be removed from ITK. Please use GraftOutput() in possible combination with DisconnectPipeline() instead." );
BaseProcess::SetNthOutput(0, output);
}
| int mitk::ImageSource::SplitRequestedRegion | ( | int | i, |
| int | num, | ||
| OutputImageRegionType & | splitRegion | ||
| ) | [protected, virtual] |
Split the output's RequestedRegion into "num" pieces, returning region "i" as "splitRegion".
This method is called "num" times. The regions must not overlap. The method returns the number of pieces that the routine is capable of splitting the output RequestedRegion, i.e. return value is less than or equal to "num".
Definition at line 111 of file mitkImageSource.cpp.
References mitk::Image::GetDimension(), mitk::SlicedData::GetRequestedRegion(), and int().
{
// Get the output pointer
OutputImageType * outputPtr = this->GetOutput();
const SlicedData::SizeType& requestedRegionSize
= outputPtr->GetRequestedRegion().GetSize();
int splitAxis;
SlicedData::IndexType splitIndex;
SlicedData::SizeType splitSize;
// Initialize the splitRegion to the output requested region
splitRegion = outputPtr->GetRequestedRegion();
splitIndex = splitRegion.GetIndex();
splitSize = splitRegion.GetSize();
// split on the outermost dimension available
splitAxis = outputPtr->GetDimension() - 1;
while (requestedRegionSize[splitAxis] == 1)
{
--splitAxis;
if (splitAxis < 0)
{ // cannot split
itkDebugMacro(" Cannot Split");
return 1;
}
}
// determine the actual number of pieces that will be generated
SlicedData::SizeType::SizeValueType range = requestedRegionSize[splitAxis];
int valuesPerThread = (int)ceil(range/(double)num);
int maxThreadIdUsed = (int)ceil(range/(double)valuesPerThread) - 1;
// Split the region
if (i < maxThreadIdUsed)
{
splitIndex[splitAxis] += i*valuesPerThread;
splitSize[splitAxis] = valuesPerThread;
}
if (i == maxThreadIdUsed)
{
splitIndex[splitAxis] += i*valuesPerThread;
// last thread needs to process the "rest" dimension being split
splitSize[splitAxis] = splitSize[splitAxis] - i*valuesPerThread;
}
// set the split region ivars
splitRegion.SetIndex( splitIndex );
splitRegion.SetSize( splitSize );
itkDebugMacro(" Split Piece: " << splitRegion );
return maxThreadIdUsed + 1;
}
| void mitk::ImageSource::ThreadedGenerateData | ( | const OutputImageRegionType & | outputRegionForThread, |
| int | threadId | ||
| ) | [protected, virtual] |
If an imaging filter can be implemented as a multithreaded algorithm, the filter will provide an implementation of ThreadedGenerateData().
This superclass will automatically split the output image into a number of pieces, spawn multiple threads, and call ThreadedGenerateData() in each thread. Prior to spawning threads, the BeforeThreadedGenerateData() method is called. After all the threads have completed, the AfterThreadedGenerateData() method is called. If an image processing filter cannot support threading, that filter should provide an implementation of the GenerateData() method instead of providing an implementation of ThreadedGenerateData(). If a filter provides a GenerateData() method as its implementation, then the filter is responsible for allocating the output data. If a filter provides a ThreadedGenerateData() method as its implementation, then the output memory will allocated automatically by this superclass. The ThreadedGenerateData() method should only produce the output specified by "outputThreadRegion" parameter. ThreadedGenerateData() cannot write to any other portion of the output image (as this is responsibility of a different thread).
Definition at line 213 of file mitkImageSource.cpp.
{
itkExceptionMacro("subclass should override this method!!!");
}
| ITK_THREAD_RETURN_TYPE mitk::ImageSource::ThreaderCallback | ( | void * | arg ) | [static, protected] |
Static function used as a "callback" by the MultiThreader.
The threading library will call this routine for each thread, which will delegate the control to ThreadedGenerateData().
Definition at line 222 of file mitkImageSource.cpp.
References mitk::ImageSource::ThreadStruct::Filter.
{
ThreadStruct *str;
int total, threadId, threadCount;
threadId = ((itk::MultiThreader::ThreadInfoStruct *)(arg))->ThreadID;
threadCount = ((itk::MultiThreader::ThreadInfoStruct *)(arg))->NumberOfThreads;
str = (ThreadStruct *)(((itk::MultiThreader::ThreadInfoStruct *)(arg))->UserData);
// execute the actual method with appropriate output region
// first find out how many pieces extent can be split into.
SlicedData::RegionType splitRegion;
total = str->Filter->SplitRequestedRegion(threadId, threadCount,
splitRegion);
if (threadId < total)
{
str->Filter->ThreadedGenerateData(splitRegion, threadId);
}
// else
// {
// otherwise don't use this thread. Sometimes the threads dont
// break up very well and it is just as efficient to leave a
// few threads idle.
// }
return ITK_THREAD_RETURN_VALUE;
}
 1.7.2
1.7.2