Difference between revisions of "MITK Plugin Style Guide"
SaschaZelzer (talk | contribs) |
SaschaZelzer (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
= The MITK Plugin Style Guide = | = The MITK Plugin Style Guide = | ||
| + | '''Attention:''' This article describes legacy [[BlueBerry]] bundles. MITK switched to using the CTK plugin framework. Although many things remain the same, this article needs to be revised. | ||
| − | This is a style guide for writing new MITK plugins. Although you could organize your files inside your plugin directory nearly arbitrarily, it is strongly advised (a nice word for mandatory) to follow this guide. | + | This is a style guide for writing new MITK plugins. Although you could organize your files inside your plugin directory nearly arbitrarily, it is strongly advised (a nice word for mandatory) to follow this guide. |
Your plugin directory should look like this (individual folders are discussed below): | Your plugin directory should look like this (individual folders are discussed below): | ||
| Line 16: | Line 17: | ||
=== Build files === | === Build files === | ||
| − | |||
Used to control build specific aspects of your plugin. | Used to control build specific aspects of your plugin. | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
=== Documentation files === | === Documentation files === | ||
| − | |||
* documentation/UserManual (optional): This is the place for your user manual. | * documentation/UserManual (optional): This is the place for your user manual. | ||
* documentation/doxygen/modules.dox (required): This file is required if your plugin contains source code. It must define two doxygen groups for your plugin, see below: | * documentation/doxygen/modules.dox (required): This file is required if your plugin contains source code. It must define two doxygen groups for your plugin, see below: | ||
| + | |||
<pre><nowiki> | <pre><nowiki> | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
\ingroup MITKPlugins | \ingroup MITKPlugins | ||
| − | \brief This is the isosurface plugin. | + | \brief This is the isosurface plugin. |
| − | + | ||
*/ | */ | ||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
*/ | */ | ||
</nowiki></pre> | </nowiki></pre> | ||
| − | |||
=== Resource files === | === Resource files === | ||
| Line 54: | Line 53: | ||
=== Source files === | === Source files === | ||
| + | * src/IsosurfaceDll.h (required): Required if your plugin contains source code. This file (the name depends on your plugin name) defines a macro containing Windows DLL export/import specifiers. You must use this macro in your class declaration (if you want your class to be accessible across DLL boundaries). | ||
| − | |||
<pre><nowiki>#!cplusplus | <pre><nowiki>#!cplusplus | ||
| − | class ISOSURFACE_EXPORTS QmitkIsoSurface | + | class ISOSURFACE_EXPORTS QmitkIsoSurface |
{ | { | ||
... | ... | ||
}; | }; | ||
</nowiki></pre> | </nowiki></pre> | ||
| − | |||
Source files should be logically grouped into two categories: Internal and External. In the beginning, usually every source and header file is internal, meaning that it is not intended to be used by other plugins/dlls/whatever. Hence it must be placed into ''src/internal''. This has nothing to do with Windows DLL export/import specifications but rather says that you do not see any benefit for others in making your classes accessible, or your code is not mature enough to be part of your plugins public API. Placing code directly under ''src'' essentially means: This code is public API, and safe for others to use (i.e. the class interfaces won't change much). | Source files should be logically grouped into two categories: Internal and External. In the beginning, usually every source and header file is internal, meaning that it is not intended to be used by other plugins/dlls/whatever. Hence it must be placed into ''src/internal''. This has nothing to do with Windows DLL export/import specifications but rather says that you do not see any benefit for others in making your classes accessible, or your code is not mature enough to be part of your plugins public API. Placing code directly under ''src'' essentially means: This code is public API, and safe for others to use (i.e. the class interfaces won't change much). | ||
| Line 73: | Line 71: | ||
Furthermore, you must put every class inside the appropriate doxygen group. For internal classes, this looks like | Furthermore, you must put every class inside the appropriate doxygen group. For internal classes, this looks like | ||
| + | |||
<pre><nowiki>#!cplusplus | <pre><nowiki>#!cplusplus | ||
| Line 78: | Line 77: | ||
\ingroup org_mitk_gui_qt_isosurface_internal | \ingroup org_mitk_gui_qt_isosurface_internal | ||
*/ | */ | ||
| − | class MyInternalClass | + | class MyInternalClass |
{ | { | ||
... | ... | ||
| Line 85: | Line 84: | ||
and for external classes | and for external classes | ||
| + | |||
<pre><nowiki>#!cplusplus | <pre><nowiki>#!cplusplus | ||
| Line 90: | Line 90: | ||
\ingroup org_mitk_gui_qt_isosurface | \ingroup org_mitk_gui_qt_isosurface | ||
*/ | */ | ||
| − | class ISOSURFACE_EXPORTS MyExternalClass | + | class ISOSURFACE_EXPORTS MyExternalClass |
{ | { | ||
... | ... | ||
}; | }; | ||
</nowiki></pre> | </nowiki></pre> | ||
Revision as of 01:38, 6 July 2011
The MITK Plugin Style Guide
Attention: This article describes legacy BlueBerry bundles. MITK switched to using the CTK plugin framework. Although many things remain the same, this article needs to be revised.
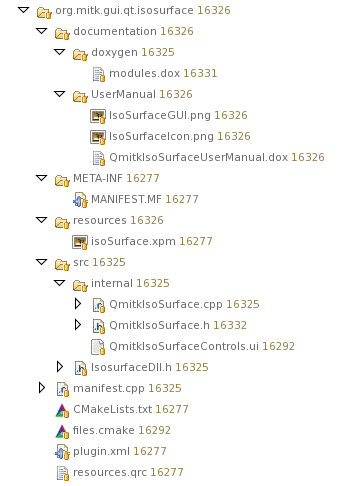
This is a style guide for writing new MITK plugins. Although you could organize your files inside your plugin directory nearly arbitrarily, it is strongly advised (a nice word for mandatory) to follow this guide.
Your plugin directory should look like this (individual folders are discussed below):
Meta files
These are files containing information about your plugin (id, name, version, extensions, ...). Click on the names of the files to get more information.
- META-INF/MANIFEST.MF (required): This file is required to have exactly this name and to be located in this folder.
- plugin.xml (optional): You need this file if you want to use extension-points or declare your own. If you don't know what this means, you won't need that file. Must be located under the plugins root directory.
- manifest.cpp (optional): This file contains code which makes your classes known to the platforms dynamic class loader. You need this file if you are using extension-points.
Build files
Used to control build specific aspects of your plugin.
- CMakeLists.txt (required): This is the entry-point for CMake. You only need to change this file if you have dependencies on external libraries (not included in plugins).
- files.cmake (optional): List your source and resource files here.
- includes.cmake (optional, not in screenshot): Inside this file, you can set the CMake variable ADDITIONAL_INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES to a list of directories which are added as include paths to dependent plugins.
Documentation files
- documentation/UserManual (optional): This is the place for your user manual.
- documentation/doxygen/modules.dox (required): This file is required if your plugin contains source code. It must define two doxygen groups for your plugin, see below:
/** \defgroup org_mitk_gui_qt_isosurface org.mitk.gui.qt.isosurface Plugin \ingroup MITKPlugins \brief This is the isosurface plugin. */ /** \defgroup org_mitk_gui_qt_isosurface_internal Internal \ingroup org_mitk_gui_qt_isosurface \brief This subcategory includes the internal classes of the org.mitk.gui.qt.isosurface plugin. Other plugins must not rely on these classes. They contain implementation details and their interface may change at any time. We mean it. */
Resource files
Resource files are usually all files which are not source-code files but are necessary for your code at runtime. They belong into the resources folder.
- resources.qrc (optional): if you use Qt, you may want to list your resource files here.
Source files
- src/IsosurfaceDll.h (required): Required if your plugin contains source code. This file (the name depends on your plugin name) defines a macro containing Windows DLL export/import specifiers. You must use this macro in your class declaration (if you want your class to be accessible across DLL boundaries).
#!cplusplus
class ISOSURFACE_EXPORTS QmitkIsoSurface
{
...
};
Source files should be logically grouped into two categories: Internal and External. In the beginning, usually every source and header file is internal, meaning that it is not intended to be used by other plugins/dlls/whatever. Hence it must be placed into src/internal. This has nothing to do with Windows DLL export/import specifications but rather says that you do not see any benefit for others in making your classes accessible, or your code is not mature enough to be part of your plugins public API. Placing code directly under src essentially means: This code is public API, and safe for others to use (i.e. the class interfaces won't change much).
Summary:
- src: Code intended to be used by others (for example in order to extend your plugin). Every class declaration must contain the DLL export/import macro.
- src/internal: Internal implementation code not to be used by others. Class declarations may contain the DLL export/import macro.
Furthermore, you must put every class inside the appropriate doxygen group. For internal classes, this looks like
#!cplusplus
/*!
\ingroup org_mitk_gui_qt_isosurface_internal
*/
class MyInternalClass
{
...
};
and for external classes
#!cplusplus
/*!
\ingroup org_mitk_gui_qt_isosurface
*/
class ISOSURFACE_EXPORTS MyExternalClass
{
...
};